Mammalogy lecture notes typically cover the essentials of mammalian biology. You’ll find information on classification, evolution, and the diverse groups of mammals. They’ll explore mammalian anatomy, physiology, and unique adaptations like hair and milk production. Behavioral ecology, including foraging strategies and social structures, is another key topic. You’ll learn about the incredible biodiversity of mammals and their various adaptations to different environments. Conservation and management strategies are often discussed, highlighting the importance of preserving mammalian species and their habitats. Dive deeper to uncover the fascinating world of mammals and their critical role in ecosystems.
Mammalian Classification and Evolution

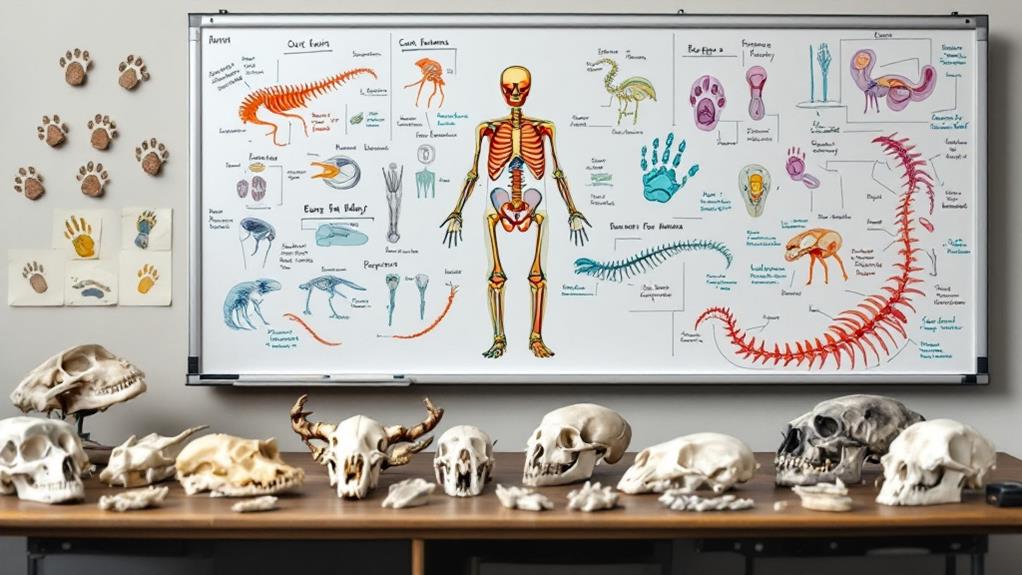
One of the most fascinating aspects of mammalogy is the study of mammalian classification and evolution. You’ll find that mammals are classified within the phylum Chordata and the class Mammalia. This classification is based on shared characteristics like hair, milk production, and a neocortex.
Mammals are divided into three main groups: monotremes, marsupials, and placentals. Monotremes, like the platypus, lay eggs. Marsupials, such as kangaroos, give birth to underdeveloped young. Placentals, which include humans, have a placenta for fetal development.
The evolution of mammals is a complex journey spanning millions of years. You’ll learn that mammals evolved from synapsids, a group of amniotes that diverged from sauropsids (reptiles and birds) about 320 million years ago. The first true mammals appeared during the Triassic period, around 225 million years ago.
Key evolutionary adaptations in mammals include endothermy (warm-bloodedness), specialized teeth, and a four-chambered heart. These features allowed mammals to thrive in diverse environments and eventually dominate many ecological niches.
You’ll explore how mammals diversified rapidly after the extinction of dinosaurs 66 million years ago. This event, known as the K-Pg extinction, opened up new opportunities for mammalian evolution. Today, there are over 6,400 known mammal species, ranging from tiny shrews to massive whales.
Understanding mammalian classification and evolution is essential for grasping the intricate relationships between different species and their adaptations to various environments. It’s a cornerstone of mammalogy that informs conservation efforts and our understanding of biodiversity.
Anatomy and Physiology
The study of mammalian anatomy and physiology is essential for understanding how these diverse creatures function. You’ll find that mammals share several key anatomical features, including hair or fur, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands. These characteristics set them apart from other vertebrates and have contributed to their evolutionary success.
When examining mammalian anatomy, you’ll notice that their skeletal structure is highly adapted to various lifestyles. For instance, you’ll see differences in limb structure between terrestrial, aquatic, and flying mammals. The muscular system is equally diverse, with adaptations for different locomotion types and specialized behaviors.
Mammalian physiology is complex and efficient. You’ll observe that mammals are endothermic, maintaining a constant body temperature through internal mechanisms. This allows them to remain active in various environments. Their circulatory system features a four-chambered heart, which efficiently pumps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood separately.
You’ll find that the respiratory system of mammals is highly developed, with alveoli in the lungs providing a large surface area for gas exchange. Their digestive system varies depending on diet, with herbivores having longer, more complex digestive tracts than carnivores.
The mammalian nervous system is advanced, with a large brain relative to body size. You’ll note that this contributes to their complex behaviors and ability to learn. Finally, you’ll discover that the reproductive system of mammals is unique, featuring internal fertilization and, in most cases, live birth. This, combined with parental care, has been vital to their evolutionary success.
Behavioral Ecology

Behavioral ecologists study how mammals interact with their environment and each other. They focus on understanding the evolutionary and ecological factors that shape animal behavior. You’ll learn about various aspects of mammalian behavior, including foraging strategies, mating systems, and social organization.
When studying foraging behavior, you’ll examine how mammals search for, locate, and consume food resources. This includes concepts like optimal foraging theory, which predicts how animals maximize energy intake while minimizing costs. You’ll also explore different feeding strategies, such as browsing, grazing, and predation.
Mating systems in mammals vary widely, from monogamy to polygamy and promiscuity. You’ll investigate the factors influencing these systems, including resource distribution, population density, and sexual selection. Understanding parental care strategies is essential, as they impact offspring survival and reproductive success.
Social behavior is another key area of study. You’ll learn about group living, dominance hierarchies, and cooperative behaviors. These aspects are important for comprehending how mammals navigate complex social environments and form alliances.
Communication plays a significant role in mammalian behavior. You’ll explore various modes of communication, including visual, auditory, olfactory, and tactile signals. Understanding how mammals convey information about territory, mating status, and potential threats is essential for interpreting their behaviors.
Lastly, you’ll examine how environmental factors influence mammalian behavior. This includes studying habitat selection, migration patterns, and responses to predation risk. You’ll also learn about behavioral adaptations to different climates and ecosystems, which are important for understanding mammalian distribution and survival strategies.
Adaptations and Biodiversity
Adaptations are the cornerstone of mammalian survival and success across diverse environments. You’ll find that mammals have evolved a wide range of physical, physiological, and behavioral adaptations to thrive in various habitats. These adaptations can be structural, like the streamlined bodies of aquatic mammals or the large ears of desert-dwelling species for heat dissipation. They can also be physiological, such as the ability of some mammals to hibernate or enter torpor to conserve energy during harsh conditions.
Biodiversity in mammals is astounding, with over 6,400 known species spanning a wide range of sizes, shapes, and lifestyles. You’ll encounter mammals in nearly every ecosystem on Earth, from the smallest shrews to the largest whales. This diversity is a result of adaptive radiation, where mammals have evolved to fill various ecological niches. For instance, you’ll see bats adapted for flight, moles for burrowing, and primates for arboreal life.
Mammalian adaptations often reflect their diet and foraging strategies. You’ll notice specialized dentition in carnivores for tearing meat, flat molars in herbivores for grinding plant material, and varied tooth structures in omnivores. Some mammals have developed unique adaptations like the long tongues of anteaters or the prehensile tails of some primates and marsupials. These adaptations not only guarantee survival but also contribute to the rich biodiversity of mammals, allowing them to occupy diverse ecological roles and maintain ecosystem balance.
Conservation and Management Strategies
Given the vast diversity and ecological significance of mammals, conservation efforts are more important than ever. You’ll find that protecting mammalian species requires a multifaceted approach, combining scientific research, policy-making, and public engagement.
To effectively conserve mammals, you must first identify threatened species and their habitats. This involves conducting population surveys, monitoring ecological changes, and evaluating human impacts. You’ll need to prioritize species based on their conservation status, ecological role, and genetic uniqueness.
Habitat preservation is essential. You should focus on establishing protected areas, wildlife corridors, and buffer zones to maintain ecosystem connectivity. It’s important to work with local communities to develop sustainable land-use practices that benefit both humans and wildlife.
Ex-situ conservation strategies, such as captive breeding programs and gene banks, can help preserve genetic diversity and provide a safeguard against extinction. You’ll need to collaborate with zoos, wildlife sanctuaries, and research institutions to implement these programs effectively.
Addressing human-wildlife conflict is another key aspect of mammal conservation. You must develop strategies to mitigate conflicts, such as implementing deterrent systems, compensating for livestock losses, and educating communities about coexistence.
Legislation and policy play an important role in mammal conservation. You should advocate for stronger wildlife protection laws, stricter enforcement of existing regulations, and international cooperation to combat illegal wildlife trade.
Lastly, public awareness and education are significant. You must engage the public through outreach programs, citizen science initiatives, and media campaigns to foster a sense of stewardship for mammalian species and their habitats.

Erzsebet Frey (Eli Frey) is an ecologist and online entrepreneur with a Master of Science in Ecology from the University of Belgrade. Originally from Serbia, she has lived in Sri Lanka since 2017. Eli has worked internationally in countries like Oman, Brazil, Germany, and Sri Lanka. In 2018, she expanded into SEO and blogging, completing courses from UC Davis and Edinburgh. Eli has founded multiple websites focused on biology, ecology, environmental science, sustainable and simple living, and outdoor activities. She enjoys creating nature and simple living videos on YouTube and participates in speleology, diving, and hiking.